Connecting to a Git Repository
Prerequisites
The following are the prerequisites for creating a Chaos Experiment:
- Fork of Chaos-Charts repository
note
An active internet connection is required to clone the git repository for the first time installation.
Connecting to a Git repository using ChaosHub
With ChaosHub, you can construct chaos experiments by selecting, tuning and sequencing different faults together from their connected ChaosHubs.
You can make changes in your forked repositories and sync it with the Portal to get the latest changes from the fork.
By default, a public ChaosHub is provided when the ChaosCenter is installed for the first time.
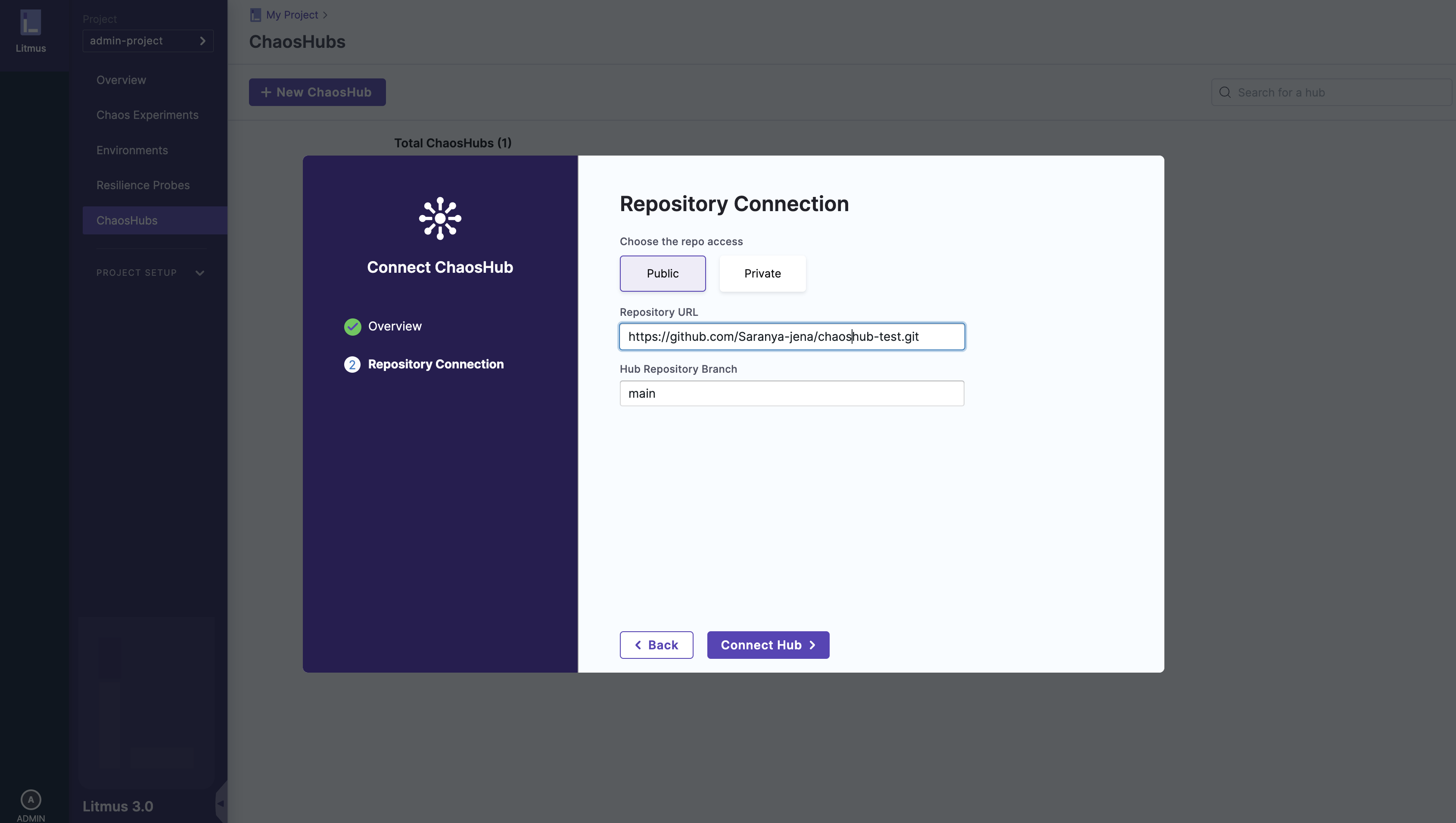
1. Connect a public Git repository
You can connect to a public Git repository by simply providing the following details:
- Hub name
- Git URL of the forked repository
- Branch name
2. Connect a private Git repository
To add a private ChaosHub, you need provide the hub name, Git URL of the forked repository and the branch name similar to that of public hub and the repository can be connected in two ways:
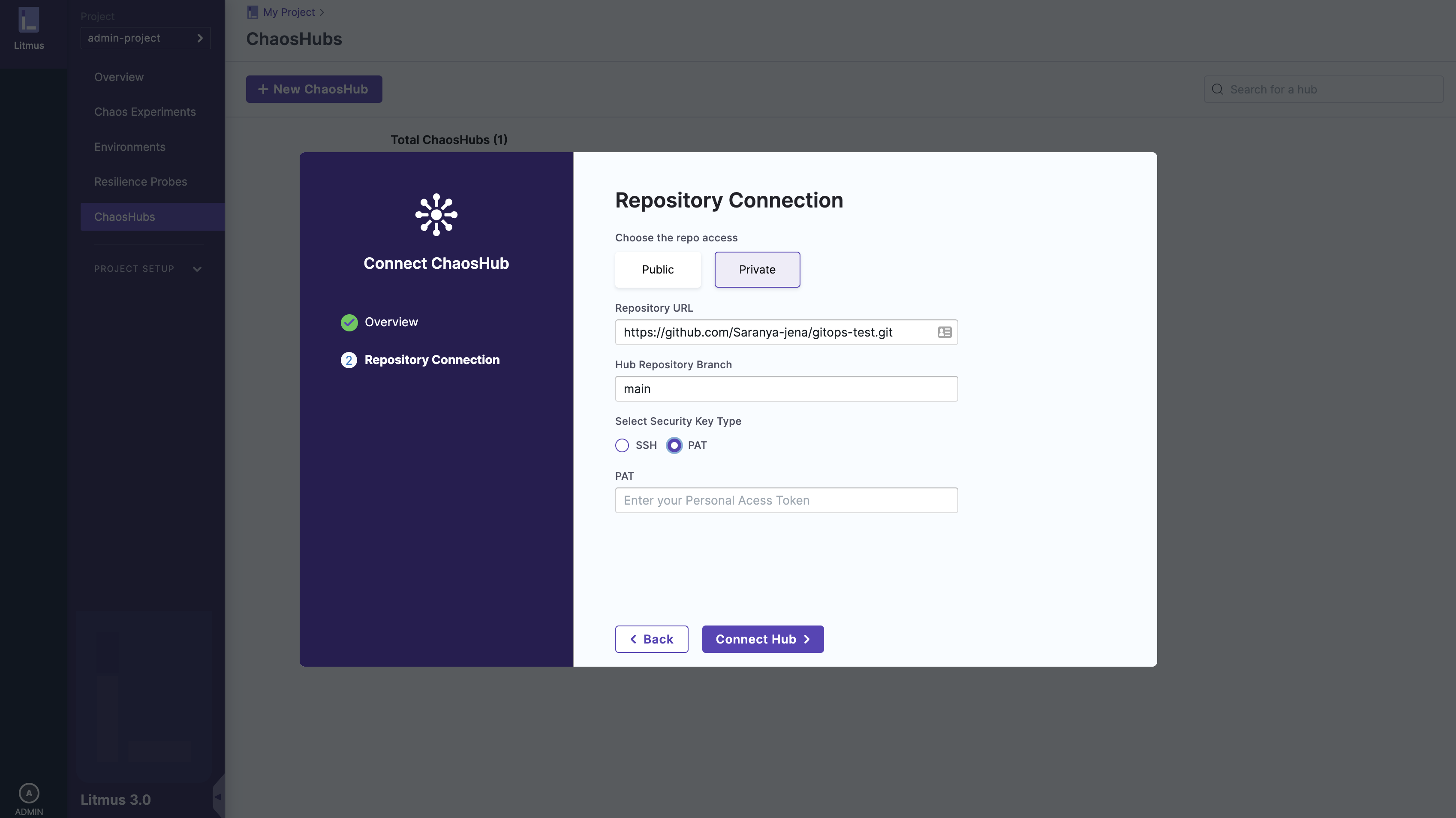
a. Access token
Personal Access Tokens are used as an alternative to the password for authentication to Git services.
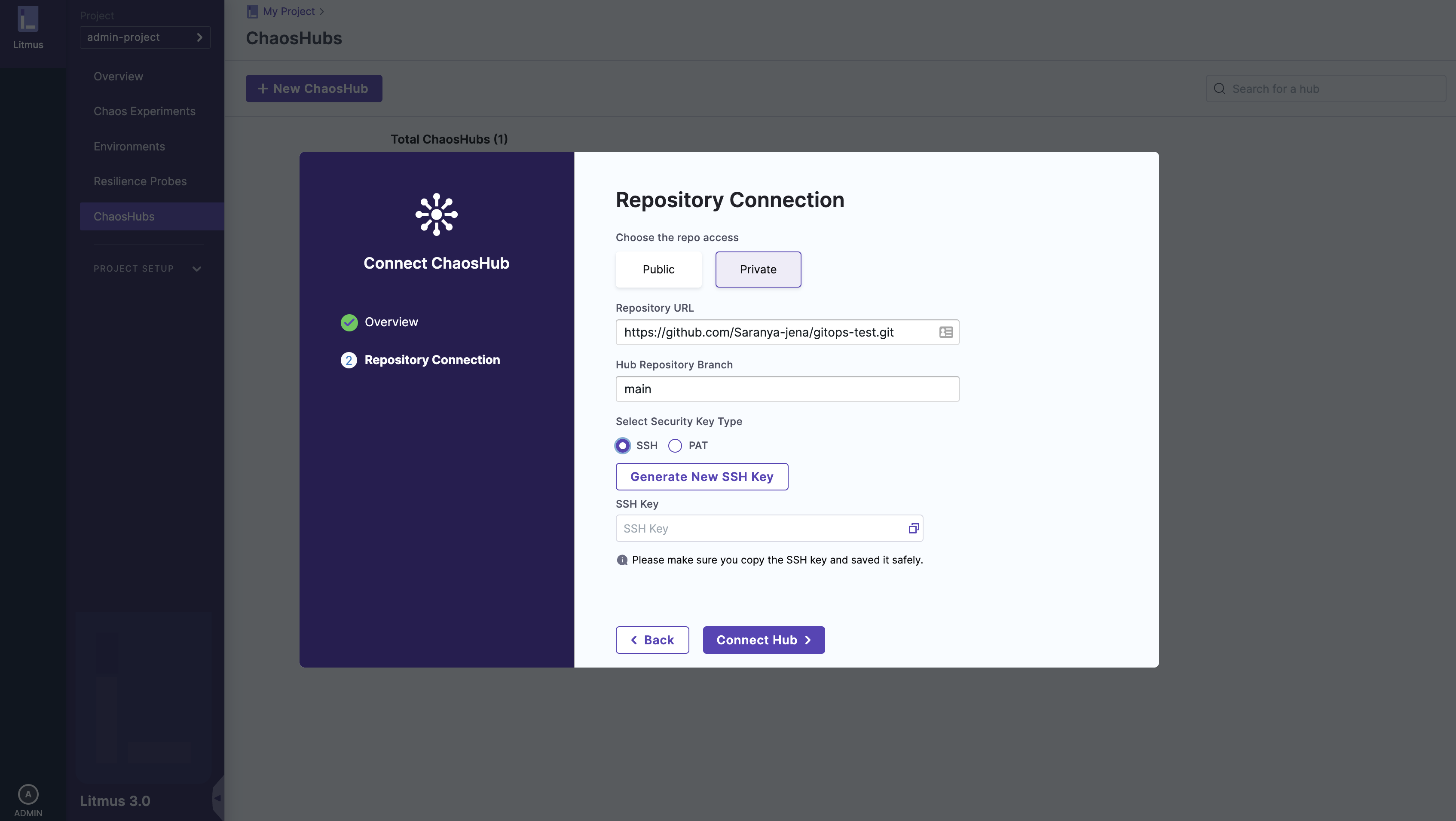
b. SSH key
Just like the Access Token , SSH keys are used for the authentication. These keys come in pairs, a public key that is shared with the Git Services and a private key that is stored with you. SSH link of the repository should be provided if you select this method.
Syncing a ChaosHub
If some changes are made into the Git repository, you can reflect these changes in the hub by selecting the Refresh Hub option from the ChaosHub card.
Editing a ChaosHub
To make changes in a hub like changing the name, branch, access token etc, you can select the Edit Hub option from the ChaosHub card.